2. what are the main features of brinell hardness test|brinell hardness test example : manufacturing The Brinell hardness test method as used to determine Brinell hardness, is defined in ASTM E10. Most commonly it is used to test materials that have a structure that is too coarse or that have a surface that is too rough to be tested . Ranking dos principais sites em janeiro 2024: confira a lista c.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da We would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us.
In this article, we have seen the Brinell hardness test and its two different methods – Standard and Non-Standard Brinell hardness tests. Also, discussed its advantages, disadvantages or limitations, and applications.
The Brinell hardness test is a widely recognized method for determining the hardness of various materials. It involves applying a constant load or force, typically ranging from 187.5 to .
Hardness in manufacturing and engineering is defined by resistance to indentation, and it is determined by measuring the permanent depth of the indentation; which is known as a hardness test. Brinell Hardness Test . I. What is the Principle of the Brinell Method? The Brinell method principle involves measuring the hardness of a material when an indenter is compressed into a test piece under .The Brinell hardness test method as used to determine Brinell hardness, is defined in ASTM E10. Most commonly it is used to test materials that have a structure that is too coarse or that have a surface that is too rough to be tested .
Brinell test procedure. In the Brinell hardness test, an optical method, the size of indentation left by the indenter is measured. In contrast to the likewise optical Vickers method,which involves .The Brinell method offers the following advantages: The Brinell method can be used for testing non-homogeneous materials (e.g. castings), because the large ball comes into contact with many crystals (different metallographic .1. Piling up: Indicates a low rate of hardening by deformation. 2. Sinking: Indicates the ability to work harden. The approximate tensile strength in PSI can be ascertained by multiplying the .The oldest of the hardness test methods in common use on engineering materials today is the Brinell hardness test. Dr. J. A. Brinell invented this test in Sweden in 1900. The Brinell test .
brinell hardness tester diagram
The Brinell hardness HBW results from the quotient of the applied test force F (in newtons N) and the surface area of the residual indentation on the specimen (the projection of the indentation) after removal of the test force (see Brinell .In metallurgy: Testing mechanical properties .oldest of such tests, the Brinell hardness test, uses a 10-millimetre-diameter ball and a 3,000-kilogram load. Brinell hardness values correlate well with UTS. The Brinell test introduced the production phase of indentation hardness testing and helped pave the way for other, more relevant hardness testing methods. And although the Brinell hardness test was the first widely .
brinell hardness test theory
An alternative method is the Brinell hardness test, which uses a hardened steel (or tungsten carbide) ball indenter with a diameter D of, usually, 10 mm.This is applied under a load P of 500–3000 kg applied for 10–30 s.The diameter of the circular indentation d is measured in millimetres. The hardness number, (HB) is calculated using the following equation: 2. Brinell hardness (1) Principle. . Main test force/N: Total test force/N: Constant K: Hardness range: application examples: A: . Improvement of hardness strength relationship and test method (1) Hardness test characteristics. ① The stress state is very soft (α>2), which is widely applicable;
There are two common methods applied to measure material hardness macroscopically: Rockwell and Brinell. Rockwell hardness differs from Brinell hardness testing in that the indentation size is measured in Brinell testing while Rockwell hardness is determined by the depth of the indentation made by a constant applied load.D2 HBW Brinell hardness 5 Test Force Surface area of indentation 5 2F kgf . for a description of the machine’s characteristics, limitations, and respective operating procedures. 5.2.2 Anvils—An anvil, or specimen support, should be used that is suitable for the specimen to be tested. The seating
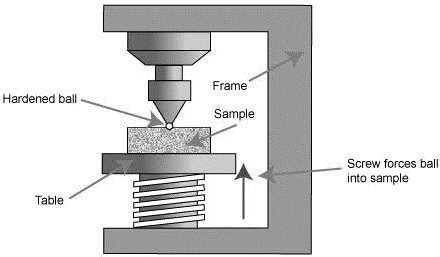
DEFINITION OF THE BRINELL HARDNESS TEST The Brinell hardness test was originally developed in the late 1800s by the Swedish engineer of the same name. He wanted to find a method to control the quality/hardness of steel. His solution was to press a railway wheel-bearing ball into the material and then measure the size of the mark it left.Brinell microscope; Indentors (2.5mm and 5mm ball) Brinell Test Machine Description. The Brinell Hardness Tester consists of a loading system, the main screw, and a dial gauge. The loading system consisting of weights, leavers and a hydraulic dashpot and a plunger arrangement is enclosed in the cast iron body of the machine. The main screw is .Hardness is the property of a material that enables it to resist plastic deformation, usually by penetration. However, the term hardness may also refer to resistance to bending, scratching, abrasion or cutting.
Brinell hardness test is one of indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested. . Main purpose of this website is to help the public to learn some interesting and important information about .While the Brinell hardness test is widely used in the industry today, some features which make it unique are worth mentioning. Firstly, it enjoyed standardization before any other method was standardized which also accounts for why it is widely used. . The main test is straightforward to perform. The diamond indenter size is not considered in .There is a formula that can help you calculate the hardness of a material based on the Brinell method. It is: BHN = 2 P / (π D (D – (D2 – d2)1/2)) Where: BHN = Brinell hardness number. P = the load on the indenting tool (kg) D = the diameter of steel ball (mm) d = measure diameter at the rim of the impression (mm) Brinell hardness numbers .
The Brinell hardness test method as used to determine Brinell hardness, is defined in ASTM E10. Most commonly it is used to test materials that have a structure that is too coarse or that have a surface that is too rough to be tested using another test method, e.g., castings and forgings. Brinell testing often use a very high test load (3000 . Hardness testing methods: Rockwell, Brinell and microhardness Heat treating has evolved into a highly complex, precise process that improves characteristics of metal parts. A critical component of quality heat treating is .A versatile Vickers, Knoop and Brinell micro/macro hardness tester, with semi/fully-automatic features for excellent repeatability over a wide load range. . How to use the Brinell hardness test for large samples with a coarse or .
measurement of fluid film thickness
Main Menu 2. Main Menu 3. Reduce risk and maintain compliance with our specialist risk management services. . The Brinell hardness test is known for its wider indentation that covers a larger surface area, providing a more .
Brinell Hardness Testing: . Incorrect Test Force: Any discrepancy in the applied test force (preload or main load) can lead to inaccurate results. Regular calibrations are essential. . The real power of hardness testing lies in its ability to provide a complete overview of the material's characteristics - an insight into its mechanical . The Brinell hardness test uses a spherical indenter which is pressed, by a precisely controlled force – most commonly 3,000 kgf – into the material being measured. The force builds between two and eight seconds then is sustained for several more to ensure that the indentation is a plastic deformation (see footnote). The diameter of the . The HRB scale typically is used for soft materials such as aluminum and brass alloys. It uses a 1/16-in. ball indenter with a 100-KG test force. Brinell Testing. Brinell testing normally is used for larger, heavy-walled pipe. Because the Brinell test is not a depth-measuring technique, it is more forgiving.
The Brinell hardness test measures material hardness by determining the diameter of an indentation made by a hardened steel or carbide ball under a specific load. A load, typically ranging from 500 to 3,000 kgf, is applied to the material’s surface for 10-15 seconds, allowing the ball to penetrate and create an indentation. .
1.5 At the time the Brinell hardness test was developed, the force levels were specified in units of kilograms-force (kgf). Although this standard specifies the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI) as the Newton (N), because of the historical precedent and continued common usage of kgf units, force values in kgf units are provided for information . General Information about the Brinell Hardness Test. The Brinell hardness test involves pressing a hard ball indenter, usually made of tungsten carbide, into the material’s surface with a specified force. The diameter of the ball is typically 10 mm, but smaller diameters such as 2.5 mm can also be used for specific applications.
Brinell Hardness Test: This test measures the diameter of an indentation made on the surface of the material by a hard steel ball under a specific load. . Material Characteristics. Test to check material; Test hardenability; Test to confirm the process; Can be used to predict Tensile strength; 2. Functionality
7.2 The test forces given in Table 2 shall be used. 7.3 The test force shall be chosen so that the diameter of the indentation d lies between the values 0,24 D and 0,6 D. The force-diameter ratio (0,1 02x F/D2) shall be chosen according to the material .The Brinell hardness number is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14[2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten (wolfram) carbide).
2. Brinell Hardness Test. The Brinell test uses a larger spherical indenter, usually made of steel or carbide, and applies a heavy load to the material. The diameter of the indentation is measured to calculate the Brinell hardness number (HB). This method is ideal for testing softer or larger materials like cast iron and steel.
brinell hardness test pdf
Resultado da LayerFile example. The following script references a layer file and inserts a single layer named Ranger Stations into a map above an existing layer .
2. what are the main features of brinell hardness test|brinell hardness test example